What is CBT (Cognitive Behavioural Therapy)?
Written by editorial staff writer at Hola. Medically reviewed by Amira Shah, MA in Counselling Psychology, Registered Psychotherapist.

Contents

Summary: Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a form of talk therapy that helps individuals change negative thoughts and actions. It incorporates techniques like journaling, exposure therapy, and structured problem-solving to manage mental health concerns like depression and anxiety. CBT is practical, goal-driven, and often shows results quickly, making it a popular and effective treatment.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is one of the most commonly used and well-researched forms of psychotherapy. It is based on the principle that our thoughts, feelings, and actions are closely linked, and we can influence our emotions and behaviours by altering negative thought patterns. Developed in the mid-1960s by Aaron Beck, CBT has evolved into a highly successful approach for addressing several mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety disorders, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
What is CBT?
CBT, or Cognitive Behavioural Therapy, is a form of talk therapy that helps people change their negative thought patterns and behaviours. It focuses on the concept that emotions, thoughts, and actions are connected, and changing thinking patterns can lead to positive emotional and behavioural change.How does CBT work? The therapeutic process
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a systematic and goal-oriented type of psychotherapy designed to assist individuals in recognising and altering unhelpful thought patterns and behaviours. The process generally starts with an evaluation, during which the therapist and client discuss the issues and establish treatment objectives. Therapy sessions concentrate on identifying negative thoughts, scrutinising them with evidence, and substituting them with healthier, more balanced perspectives. Clients acquire practical coping techniques, such as relaxation methods and problem-solving approaches, which they can implement daily. Assignments between sessions help reinforce these skills. It is commonly utilised to address anxiety, depression, stress, and various other mental health disorders. With persistent effort, CBT can yield long-lasting improvements.Also read: What Is Online Therapy? Everything You Need To Know About e-Therapy
Ready for positive change? Start your mental health care plan here.
What happens in CBT sessions?
CBT sessions are organised and aimed at achieving specific goals. During the initial sessions, your therapist will inquire about your concerns, thoughts, feelings, and behaviours. Together, you will establish clear objectives for therapy. Each session generally includes discussing recent experiences, recognising negative thought patterns, and learning how to contest and replace them with more constructive ones.
You will also acquire practical coping methods such as relaxation, exposure techniques, behavioural activation, or problem-solving. Therapists frequently assign "homework" to reinforce these skills between sessions. Progress is regularly evaluated, and the therapist helps you implement what you've learned in daily life. CBT is engaging, meaning you collaborate closely with your therapist to enhance self-awareness and cultivate long-term mental health skills.
Types of cognitive behavioural therapy
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) encompasses several specialised forms that cater to various mental health requirements. Here are some important types:- Traditional CBT: Concentrates on recognising and disputing negative thought patterns and behaviours.
- Dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT): Combines CBT with mindfulness, distress tolerance emotion regulation and interpersonal effective skills. Originally developed for individuals with borderline personality disorder, it is also beneficial for those with borderline personality disorder and emotional instability.
- Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT): Promotes accepting thoughts and feelings instead of resisting them, while committing to personal values. While related to CBT, ACT is considered part of the “third wave” of behavioural therapies and has distinct philosophical underpinnings.
- Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT): Integrates mindfulness techniques to help prevent relapse in individuals with recurrent depression, particularly when they are currently in remission.
- Schema therapy: Focuses on addressing deeply ingrained patterns (schemas) developed in childhood that influence adult behaviour and emotions. It integrates elements of CBT, attachment theory and psychodynamic concepts, and is often used for individual with chronic mental health issues or personality disorders.
Also read: Talking to your doctor (GP) about mental health: A therapist guide
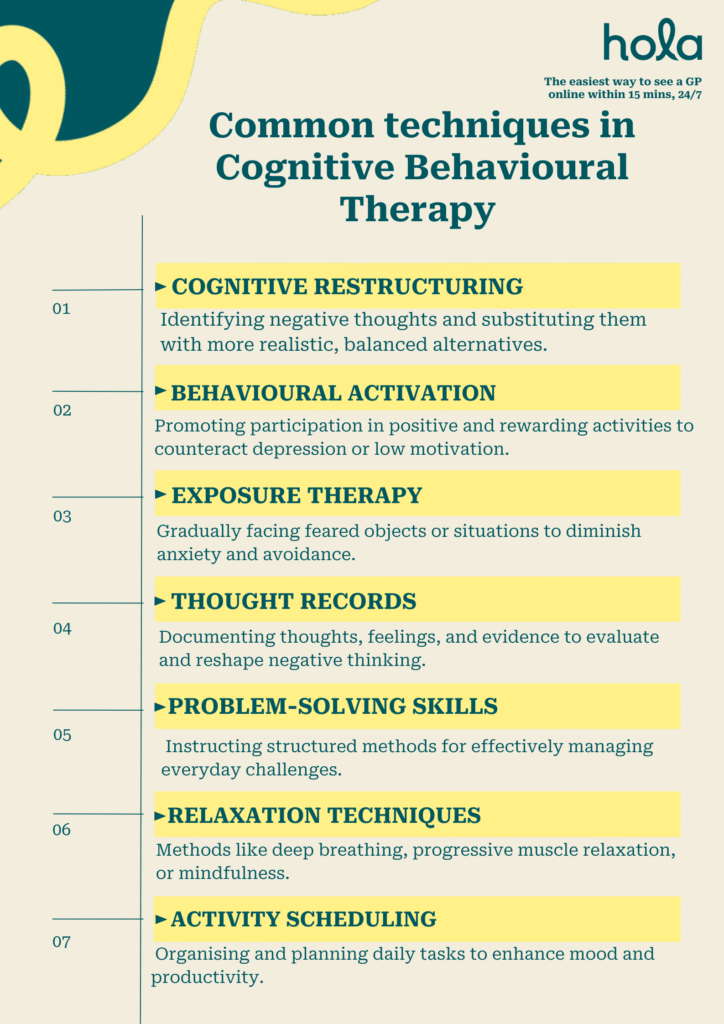
Common techniques used in Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
CBT comprises a variety of practical methods aimed at helping individuals recognise, question, and transform unhelpful thought patterns and behaviours. Some commonly employed techniques include:
- Cognitive restructuring: Identifying negative thoughts and substituting them with more realistic, balanced alternatives.
- Behavioural activation: Promoting participation in positive and rewarding activities to counteract depression or low motivation. It is especially effective for treating depression by increasing engagement with valued life activities.
- Exposure therapy: Gradually facing feared objects or situations to diminish anxiety and avoidance. This technique is most often used to treat anxiety, including phobias, social anxiety disorder and PTSD.
- Thought records: Documenting thoughts, feelings, and evidence to evaluate and reshape negative thinking. This helps individuals identify cognitive distortions and challenge inaccurate or harmful beliefs.
- Problem-solving skills: Instructing structured methods for effectively managing everyday challenges.
- Relaxation techniques: Methods like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness to alleviate stress. These techniques are often used in conjunction with CBT to help manage physiological symptoms of anxiety.
- Activity scheduling: Organising and planning daily tasks to enhance mood and productivity. This is particularly useful in treating depression, where individual may struggle with low motivation and anhedonia.
By consistently applying its techniques, such as cognitive restructuring, exposure therapy, and problem-solving, CBT empowers individuals to disrupt negative cycles and elevate their mental health. With support from a qualified therapist, these strategies can result in long-term positive changes and increased emotional resilience.

What Cognitive Behavioural Therapy can help with
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a flexible and research-supported method that effectively addresses several mental health challenges. It is frequently utilised for:
- Depression and anxiety disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Phobias and panic attacks
- Eating disorders
- Sleep disturbances (such as insomnia)
- Stress and anger management
- Substance use disorders
- Chronic pain and emotional distress related to medical conditions
CBT aids individuals in identifying unhelpful thought patterns and substituting them with healthier ways of thinking and acting, enhancing overall emotional and psychological health.
The benefits and effectiveness of CBT
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective, evidence-supported method for addressing a variety of mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, PTSD, OCD, and phobias. One of its primary advantages is its well-organised, goal-focused approach, which assists individuals in recognising and challenging harmful thought patterns and behaviours. CBT equips individuals with practical coping mechanisms that can be utilised outside of therapy, fostering long-lasting mental resilience. Additionally, CBT is time-efficient, often necessitating fewer sessions than other therapeutic modalities and is adaptable for individuals, groups, or even digital applications. Research consistently indicates that CBT is as effective for many conditions and, for certain disorders (e.g. mild to moderate depression, anxiety disorders) it can be effective as medication-especially when combined with pharmacological treatment.
In summary, CBT is a flexible, validated therapy that aids individuals in developing healthier thought patterns, enhancing emotional regulation, and taking charge of their mental health.
When doesn't CBT work?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) might not be suitable for everyone or every circumstance. It can be less effective when:- The underlying issues are not cognitive: If the sources of distress are rooted in deep, trauma-related experiences or unresolved childhood matters, CBT alone may not reach those depths. In such cases, integrative approach involving trauma-focused therapies (e.g. EMDR or psychodynamic therapy) may be more effective.
- There is a lack of readiness or motivation: CBT demands active engagement and a desire to shift thought patterns. If a person is not prepared to participate, progress could be limited.
- Severe mental health issues: In situations involving psychosis, severe bipolar disorder, or advanced personality disorders, CBT might need to be supplemented with other treatments such as medication or alternative methods. While CBT can be adapted for complex conditions, it is often most effective when integrated into a broader treatment plan that includes pharmacotherapy and/or other therapeutic modalities
- Inadequate therapist-client compatibility: A lack of trust or connection with the therapist can impede the therapy process.
Is CBT the right choice for you?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) could be a suitable choice if you are facing challenges like anxiety, depression, stress, phobias, or negative thinking patterns. It is most effective for individuals willing to engage in self-reflection, set goals, and participate actively in structured sessions. However, if your difficulties arise from deep-rooted trauma or emotional pain, other therapy modalities may be more beneficial. For example, EMDR or trauma focused therapies may be better suited for processing complex trauma. A mental health professional can evaluate your situation and direct you towards the most appropriate treatment option.Getting mental health support online
Gaining access to mental health support online has become increasingly straightforward and private. Telehealth services like Hola Health enable you to connect with qualified mental health professionals from your own home. Whether you’re managing stress, anxiety, depression, or require a Mental Health Treatment Plan (MHTP), online resources offer flexible scheduling and prompt access to care. These platforms can offer therapy sessions, medical guidance, prescriptions, and referrals when necessary. Online mental health support presents a practical, discreet, and accessible means to prioritise your mental well-being, particularly when in-person appointments are challenging.Conclusion
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy is an evidence-based and proven method for helping people manage their thoughts and actions. Its structured, goal-oriented approach makes it successful in treating many mental health problems and fosters long-term emotional stability.FAQs
What mental health conditions does CBT treat?
CBT is effective in managing a wide range of mental health conditions, including:- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Phobias
- Eating disorders
- Some personality disorders (e.g. avoidant or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder; others may require different or combined approaches).
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Sleep problems like insomnia
- Symptoms associated with Attention-Deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), although CBT is usually used along side other treatments
- Substance abuse
- Chronic pain
Who is a CBT therapist?
A CBT therapist is a mental health professional who uses Cognitive Behavioural Therapy to help people understand and change negative thought patterns and behaviours. They collaborate with clients to establish personal goals, teach effective coping strategies, and guide them through practical steps to enhance emotional wellness.What is CBT therapy?
CBT, or Cognitive Behavioural Therapy, is a kind of talk therapy that helps people shift their negative thoughts and actions. It emphasises the connection between thoughts, emotions, and actions, and teaches practical skills to manage challenges like stress, anxiety, and depression. CBT often works quickly and focuses on clear goals, making it effective for many mental health problems.What does CBT stand for?
CBT stands for Cognitive Behavioural Therapy.How do I get CBT?
You can get CBT by consulting a doctor or a mental health professional who can connect you with a trained therapist. Many people also discover CBT through online directories, local health clinics, or digital therapy platforms. Some prefer self-guided books or online programs that teach CBT techniques. It’s a flexible therapy available in person and online. However, working with a trained therapist-especially for moderate to severe conditions – is generally more effective than self-guided approaches.What CBT techniques are used for depression?
For depression, CBT uses techniques like cognitive restructuring to address negative thought patterns, behavioural activation to promote meaningful activities, and problem-solving to improve coping and decision-making. Activity scheduling encourages engaging in positive tasks, while problem-solving equips individuals to cope with tough situations, all aimed at improving mood and alleviating depressive symptoms. Graded exposure is more commonly used for anxiety and phobias rather than depression.What are CBT exercises for ADHD?
CBT exercises for ADHD aim to improve focus, organisation, and impulse control. Techniques include cognitive restructuring to challenge negative thoughts, time management strategies such as timers and task breakdowns, and behavioural activation to encourage participation in planned activities. Mindfulness helps boost attention, and learning organisational skills helps with task management and reduces clutter. These strategies are designed to alleviate ADHD symptoms and improve daily functioning. While CBT does not treat core ADHD symptoms directly, it can help with related emotional and functional challenges.What is CBT testing?
CBT testing is a way to check if your thoughts are true or helpful. With your therapist, you look at the evidence for and against a thought—like asking, “Is this really always true?” This helps you replace negative thoughts with more balanced ones. It’s not a test you pass or fail—just a tool to help you think more clearly and feel better.Can CBT be done on your own?
Yes, CBT can be practised independently using self-help books, online programs, or workbooks. These resources show you how to spot negative thoughts, handle emotions, and change problematic behaviours. Self-directed CBT can be helpful for mild to moderate symptoms, but more severe mental health conditions may require guidance from a qualified professional.Can CBT help with ADHD?
Yes, CBT can help in managing ADHD by teaching practical skills for time management, organisation, and impulse control. It emphasises changing unproductive thought patterns and establishing structured habits that support focus and productivity. CBT is especially beneficial for adults with ADHD and is often used alongside medication and coaching strategies for better results.Can CBT help with autism?
Yes, CBT can help individuals with autism, especially in addressing mood disorders, social difficulties, and anxiety. It is often adapted to match the person’s communication preferences and cognitive style. CBT teaches ways to cope, manage emotions, and address negative thoughts, making it a valuable tool when modified appropriately to suit the individual’s developmental and cognitive needs.Can CBT help with depression?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment for depression. It works by helping individuals recognise and change the negative thought patterns and behaviours that lead to a low mood. It is widely recommended as a first-line treatment, especially for mild to moderate depression, and can also be combined with medication when needed.What are the steps of CBT?
The steps of CBT usually involve:- Assessment
- Education
- Cognitive restructuring
- Behavioural activation
- Skill development
- Practice and homework
- Review and self-reflection
Do I need a referral to see a CBT therapist?
You do not usually need a referral to see a CBT therapist. You can contact a certified therapist directly. However, if you intend to use Medicare or private health insurance to cover the cost, you will need a referral from a general practitioner (GP). The GP can prepare a Mental Health Care Plan, which allows you to access discounted therapy sessions under the Better Access initiative.Take control of your mental health. Begin your care plan now.
Reference
- National Library of Medicine - reference link
- Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care - reference link
What we treat
- Cough
- Nausea & vomiting
- Fever
- Hayfever
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Gout
- Eczema
- Rosacea
- Sunburn
- UTI
- Erectile dysfunction
- Contraception
- Morning sickness
- Morning after pill
- Prostate health
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Stress
- Grief & loss
- Antidepressants
- Premature ejaculation
- Asthma
- Blood pressure
- Blood thinners
- Diabetes
- Cholesterol
- Migraines & headaches
- Allergies
- Body ache
- Heartburn & reflux
- Sleep disorder
- Pain relief
- Gastro
Related Articles
Disclaimer
This blog is for general informational purposes only and does not indicate that Hola Health provides all treatments or preventive measures mentioned. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. For emergencies please immediately contact 000. Any medical topics discussed are intended to educate, not to imply availability through Hola Health.

Get affordable healthcare on your terms, with quick access to qualified, Australian-registered telehealth doctors & health practitioners, 24/7, 365 days a year. No more searching for ‘doctors near me‘ – Hola connects you instantly.
Address: 79 St Georges Terrace, Perth WA 6000


Hola Health App
Get affordable healthcare on your terms, with quick access to qualified, Australian-registered telehealth doctors & health practitioners, 24/7, 365 days a year. No more searching for ‘doctors near me‘ – Hola connects you instantly.
Call 000 for emergency or urgent medical help.
Address: 79 St Georges Terrace, Perth WA 6000
© Hola Health, a brand of Packapill Pvt Ltd


 Facebook
Facebook  X
X  Copy Link
Copy Link